(!)Due to Microsoft's end of support for Internet Explorer 11 on 15/06/2022, this site does not support the recommended environment.
- Penghentian penjualan kategori produk pneumatik Seri Ekonomi (E-series). Info Detail
Notice of End of Sales for Economy Series Pneumatic Equipment Category. More information.
Timing Belt and Pulleys
Sizing Timing Belts and Pulleys
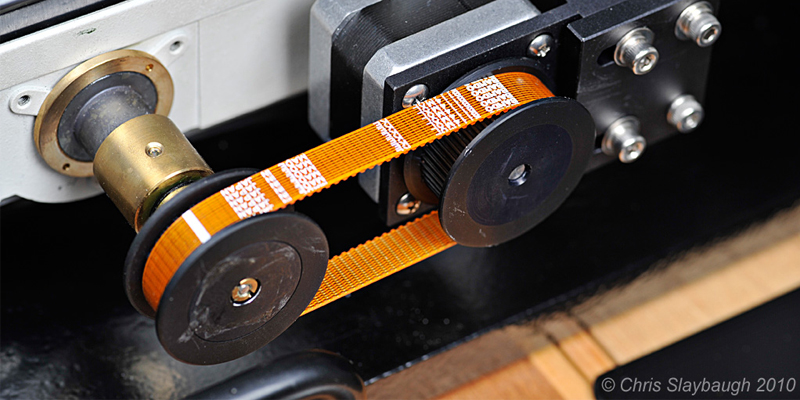
Timing Belt and Pulley Image from Photomacrography
MISUMI have been contacted by customers for question below :
Q : "Dear MISUMI Technical Support Team,
We are building a machine that has several shafts driven by stepper motors. These shafts need to be synchronized to each other, but at different speeds. We did some research and it looks like a timing belt system will solve our problem, but we don’t know how to proceed with selecting parts. Could you please provide some tips or recommendations?"
MISUMI is always happy to give advice on various products for machines that need to work in relation to the various parts.
A: With any synchronization project, it’s all about the timing. Let’s start with a brief introduction on timing belts, pulleys, and how they work together
A timing belt is used when the rotation of two different shafts need to be exactly linked. Normal power transmission belts and pulleys are smooth, so the belt can occasionally slip off track (one shaft would be turning while the other remains still). On the other hand, timing belts and pulleys have teeth, which lock the rotation of the shafts and prevent misalignment. In a car, the timing belt links the engine crankshaft to the valve camshaft, thereby making sure that the valves open and close at the correct times. If that belt tears or breaks a tooth, the valves can open at the wrong time and ruin the engine.
There are a lot of different variables for belt sizing – width, number of teeth (pitch), material, etc. Each manufacturer will have different recommendations based on your project’s specifications, taking into account shaft speeds, power transmission, environment, and other concerns. Take care not to needlessly oversize – a larger, stiffer belt can cause difficulties with smaller drive motors.
As with any belt and pulley system, you need to identify the rotation ratio between the shafts. For instance, if shaft #1 needs to spin twice as fast as shaft #2, you would have a 2:1 ratio. Once this ratio is calculated, you can then select the pulleys. Looking at the number of teeth on the pulley, find two that match your desired ratio. Continuing with our example, if we had a 16-tooth pulley on shaft #1, we would need a 32-tooth pulley on shaft #2.
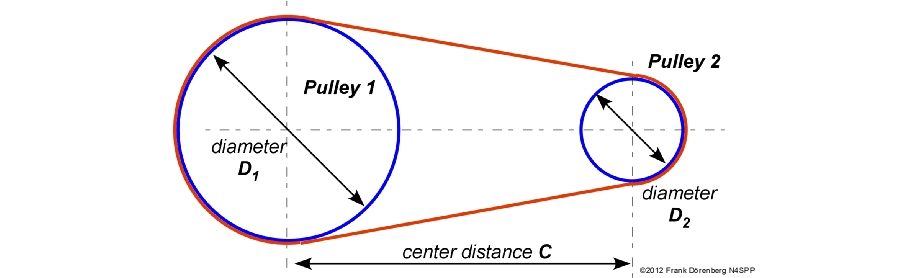
Figure showing belt length from Nonstop Systems
The next tricky part of the design is figuring out the belt length. You need to know the distance between the centers of the two shafts and the pitch diameters of the two pulleys, which is usually specified by the manufacturer. Most belt manufacturers will provide an online calculator for finding lengths of their belts, but the following formulas can be used to calculate belt length:
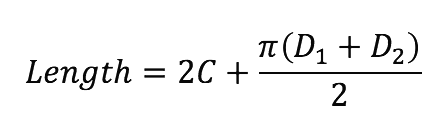
If you need an exact measurement, you can use the following formula:
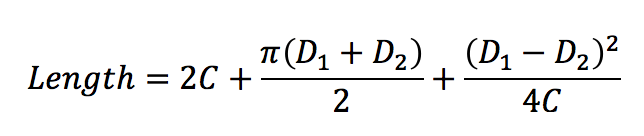
where:
- • C : Center to center distance between shafts
- • D1 : Pitch diameter of larger pulley
- • D2 : Pitch diameter of smaller pulley
Note that these formulas don’t take into consideration any pretension on the belt – most recommendations are for 1% – 8%. Belts are only made in certain lengths, so you may need to slightly adjust shaft spacing or pulley diameters to find one that works for you.
Now, all of your system components should be in place. We’ve identified the proper belt type based on the system requirements and manufacturer recommendations, sized the pulleys to the correct shaft ratio, and calculated the belt length.
Put everything together, and you’ve got a fine tuned machine which work perfectly.
Timing belt
-

270H075G

-

60S3M1050G

-

30T8012.7

-

100S2M80G

-

HTBO-S5M250-500

-

HTBN1000S5M-100

-

TBCR-S5M150

-

TTBU1000T10-250

 Need support regarding products ? Contact us, We ready to help you !
Need support regarding products ? Contact us, We ready to help you ! 
- Customer Service
-
- Adjust delivery date
- Change your ordering
- Give advice on How to use eCatalog
- Give advice on How to ordering online
- 021-8984-0008
- cs@misumi.co.id
- Technical Support
-
- Give advice on How to choose items
- Compare item code
- Item information
- Technical information/3D CAD
- 021-2918-1730
- tech-support.fv@misumi.co.id
See related content
- Timing Pulley, IdlersRecommendation Timing Pulley, Idlers from MISUMI.Available in many specifications.
- Timing beltPopular product of Timing Belt from MISUMI. Same day delivery is available.
- Round Belts, PulleysRecommendation Round Belt from MISUMI. Required length can be selected.
MISUMI 5 Benefits
Have you ever got a problem with ordering? Click here and let us help you!





 Automation Components
Automation Components
 Fasteners
Fasteners
 Materials
Materials
 Wiring Components
Wiring Components
 Electrical & Controls
Electrical & Controls
 Cutting Tools
Cutting Tools
 Processing Tools
Processing Tools
 Material Handling & Storage
Material Handling & Storage
 Safety & General Supplies
Safety & General Supplies
 Lab & Clean Room Supplies
Lab & Clean Room Supplies
 Press Die Components
Press Die Components
 Plastic Mold Components
Plastic Mold Components
 Injection Molding Components
Injection Molding Components